Generac RS5500 Manual: A Comprehensive Guide
This guide provides detailed instructions for the Generac RS5500‚ covering safety‚ operation‚ maintenance‚ and troubleshooting. Refer to this manual for optimal performance and longevity.
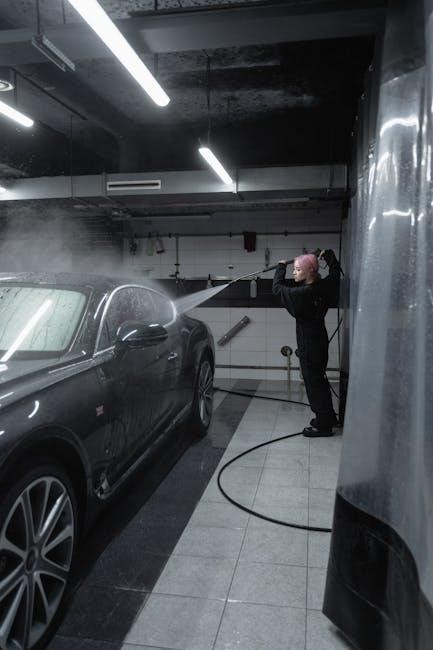
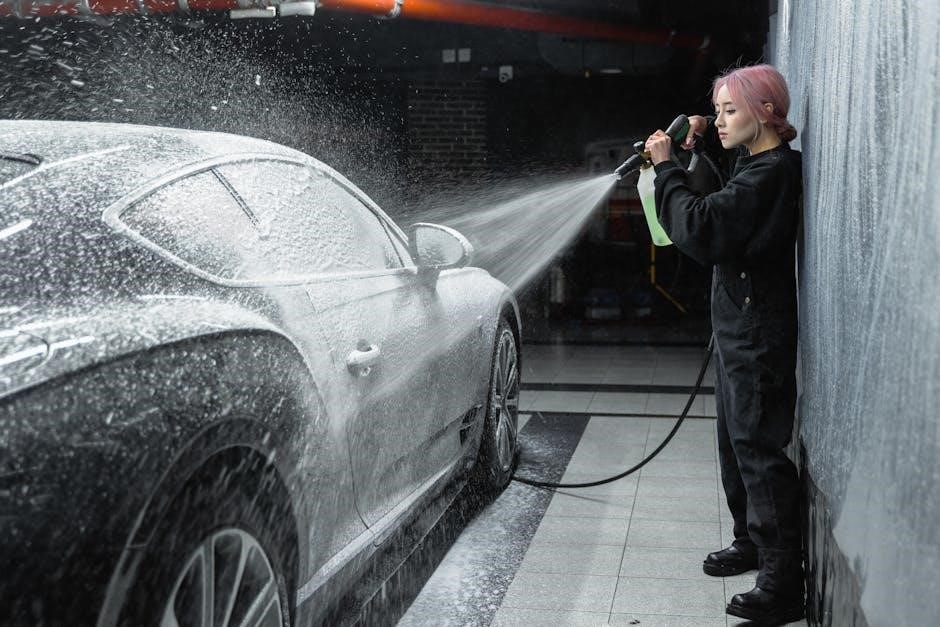
The Generac RS5500 is a portable generator designed for convenience and reliable power during outages or remote activities. This PowerDial series generator delivers 5500 starting watts and 4500 running watts‚ suitable for powering essential appliances and tools.
Important safety warnings regarding exhaust fumes and critical life support applications are paramount. This manual serves as a crucial resource for all operators‚ ensuring safe and effective use. Always prioritize referencing all documentation provided with the unit.
Safety Precautions & Warnings
WARNING! The Generac RS5500 produces deadly exhaust fumes. Never operate indoors‚ near windows‚ doors‚ or vents. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious risk. This generator is not for use in critical life support systems.
Always provide this manual to all operators and ensure they understand all safety guidelines. Keep the generator away from flammable materials. Ground the generator properly to prevent electrical shock. Save this manual for future reference.
Understanding the Generator Components
The Generac RS5500 features a robust engine and generator system. Key exterior components include the PowerDial‚ outlets‚ fuel tank‚ and recoil starter. Engine components consist of the air filter‚ spark plug‚ and carburetor. Familiarize yourself with these parts for effective maintenance.
Understanding the location and function of each component is crucial for safe operation and troubleshooting. Refer to diagrams within this manual for detailed illustrations and part identification.
Generator Exterior Features
The Generac RS5500’s exterior boasts a user-friendly design. The prominent PowerDial allows for easy starting and shutdown. Multiple outlets‚ including standard receptacles‚ provide connectivity for various devices. A secure fuel tank cap prevents spills‚ while the recoil starter enables manual starting.
The robust frame offers portability and protection. Carefully inspect these exterior features before each use‚ ensuring all components are intact and functioning correctly for safe operation.
Engine Components Overview
The Generac RS5500 utilizes a robust engine. Key components include the air filter‚ ensuring clean air intake for combustion. The spark plug ignites the fuel-air mixture‚ initiating the engine cycle. The carburetor mixes air and fuel for optimal performance.
The muffler reduces exhaust noise‚ and the recoil starter provides manual starting capability. Regularly inspect these components for wear and tear‚ maintaining peak engine efficiency and reliability.
Preparing for First Use
Before operating your Generac RS5500‚ thorough preparation is crucial. Unbox the generator and carefully inspect it for any shipping damage. Verify all components are present‚ referencing the included parts list.
Crucially‚ add the correct grade of oil as specified in the manual. Then‚ carefully add unleaded gasoline‚ ensuring proper fuel levels. These initial steps guarantee safe and reliable operation from the outset.
Unboxing and Inspection
Upon receiving your Generac RS5500‚ carefully unpack it from the shipping container. Inspect the generator for any visible damage incurred during transit – dents‚ scratches‚ or loose parts.
Compare the contents against the included parts list to ensure everything is accounted for. Document any discrepancies immediately. Retain the packaging materials for potential returns or warranty claims. A thorough inspection prevents future issues.
Adding Oil and Fuel
Before starting‚ add oil – check the manual for the correct type and quantity. Use a funnel to avoid spills. Next‚ carefully add fresh‚ unleaded gasoline‚ ensuring it’s free of contaminants. Do not overfill the fuel tank; leave space for expansion.
Always add fuel outdoors in a well-ventilated area. Wipe up any spills immediately. Using fuel stabilizer is recommended for prolonged storage to prevent fuel degradation.
Starting the Generac RS5500
Ensure the generator is on a level surface and the oil/fuel levels are correct. Turn the PowerDial to the “ON” position. For a cold start‚ set the choke to the “START” position. Pull the recoil starter cord firmly and steadily until the engine ignites. Once running‚ gradually move the choke to the “RUN” position.
For a warm start‚ the choke may not be needed. Refer to the manual for specific instructions.
Cold Start Procedure
Before initiating‚ verify sufficient oil and fuel. Turn the PowerDial switch to the “ON” position. Engage the choke by moving the control to “START”. Firmly grasp the recoil starter handle and pull slowly until resistance is felt‚ then pull briskly. Repeat if necessary until the engine starts.
Gradually return the choke to the “RUN” position as the engine warms. Consult the manual for detailed diagrams.
Warm Start Procedure
With a warm engine‚ the choke may not be required. Turn the PowerDial switch to the “ON” position. Firmly grasp the recoil starter handle and pull briskly. The engine should start with minimal effort. If it doesn’t‚ briefly engage the choke and repeat the starting process.
Avoid prolonged cranking to prevent overheating. Refer to the manual for specific guidance and safety precautions.
Operating the Generator
Before connecting any loads‚ ensure the generator is on a stable‚ level surface outdoors‚ away from flammable materials. Utilize the PowerDial to select the desired voltage and operating mode. Always start the generator before connecting appliances.
Avoid exceeding the rated wattage to prevent damage. Refer to the manual for detailed load management guidelines and safety instructions.
PowerDial Operation Explained
The PowerDial controls voltage selection and engine operation. Rotate to “OFF” to stop the generator. Turn to “RUN” for normal operation‚ and select the appropriate voltage – 120V or 240V – based on your appliance needs.
Ensure the PowerDial is fully engaged in the selected position. Refer to the manual for specific load limitations at each voltage setting. Incorrect settings can damage equipment.
Connecting Appliances & Devices
Before connecting‚ ensure appliances are in the “OFF” position. Use heavy-duty‚ outdoor-rated extension cords of the correct gauge for the amperage draw. Avoid overloading the generator; calculate total wattage requirements before connecting multiple devices.
Plug appliances directly into the generator’s outlets or the extension cord. Never backfeed power into household wiring. Refer to the manual for outlet capacity details.
Understanding the Control Panel
The Generac RS5500 control panel houses essential operating features. It includes outlets – typically 120V and potentially 240V – each with specific wattage capacities. Indicator lights display generator status‚ such as “Low Oil‚” “Overload‚” and “Ready.” The PowerDial controls generator functions.
Familiarize yourself with each component’s location and function. Refer to the manual for detailed explanations of indicator light meanings and proper PowerDial operation.
Outlet Types and Capacities
The Generac RS5500 typically features multiple outlet types‚ including standard 120V receptacles for common household appliances. Some models may also include a 120/240V outlet for higher-power devices. Each outlet has a specific amperage rating and corresponding wattage capacity.
Always check the wattage requirements of your appliances before connecting them. Do not exceed the outlet’s capacity to prevent overload and potential damage to the generator or connected devices.
Indicator Lights and Their Meanings
The Generac RS5500 control panel utilizes indicator lights to communicate the generator’s status. A “Power” light signifies the unit is running‚ while a “Low Oil” light indicates insufficient oil levels – immediately stop the engine if illuminated. The “Overload” light signals excessive power draw‚ requiring load reduction.
Understanding these lights is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Refer to the full manual for a complete list and detailed explanations of each indicator’s meaning;
Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance ensures the Generac RS5500’s reliability. Check the oil level before each use and change it after the first 25 hours‚ then every 100 hours of operation. The air filter requires cleaning after 25 hours and replacement every 150 hours.
Inspect the spark plug annually‚ cleaning or replacing as needed. Adhering to this schedule maximizes performance and extends the generator’s lifespan. Consult the full manual for detailed procedures.
Oil Change Procedure
Warm the engine briefly before draining the old oil. Locate the drain plug and remove it‚ allowing the oil to fully drain into a suitable container. Replace the drain plug securely. Add the recommended oil type and quantity‚ as specified in the manual – typically around 18 ounces.
Check the oil level with the dipstick‚ ensuring it’s within the proper range. Dispose of used oil responsibly.
Air Filter Cleaning/Replacement
Regularly inspect the air filter for dirt and debris. For paper filters‚ gently tap to remove loose particles or replace with a new filter. Foam filters can be washed with mild soap and water‚ then thoroughly dried before re-oiling lightly with air filter oil.
Ensure the filter is properly seated before reassembling the air filter housing. A clean air filter ensures optimal engine performance and prevents damage.
Spark Plug Maintenance
Periodically inspect the spark plug for fouling‚ wear‚ or damage. Clean the spark plug with a wire brush‚ or replace it with a new one of the correct type‚ as specified in the specifications section. Ensure the spark plug gap is correct before installation.
Proper spark plug maintenance is crucial for reliable starting and efficient engine operation. A faulty spark plug can cause starting difficulties and reduced power output.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If the generator fails to start‚ check the fuel level‚ oil level‚ and spark plug connection. Ensure the PowerDial is in the correct position. For low power output‚ verify the generator isn’t overloaded and the air filter is clean.
Consult the full manual for detailed diagnostic steps and safety precautions. Addressing these common issues promptly will restore optimal generator performance and prevent further complications.
Generator Won’t Start
If your RS5500 won’t start‚ first verify sufficient fuel and oil levels. Check the spark plug for fouling and ensure a secure connection. Confirm the PowerDial is positioned correctly – often to the ‘Run’ setting. Inspect the recoil starter for damage.
A flooded engine can also prevent starting; allow time for fuel to dissipate. Refer to the manual’s detailed troubleshooting section for further guidance and safety instructions.
Low Power Output
Reduced power output from your RS5500 may indicate an overloaded circuit. Ensure connected appliances’ wattage doesn’t exceed the generator’s capacity. Check the air filter for obstructions‚ as a dirty filter restricts airflow. Inspect the spark plug and carburetor for cleanliness and proper function.
Low oil levels or a faulty voltage regulator can also contribute. Consult the manual for specific troubleshooting steps and safety precautions before attempting repairs.
Fuel System Maintenance
Maintaining the fuel system is crucial for reliable operation. Always use fresh fuel and consider a fuel stabilizer‚ especially during storage‚ to prevent degradation. Regularly inspect the fuel lines for cracks or leaks‚ replacing them as needed. A clogged carburetor can cause starting issues and reduced performance.
Periodically clean the carburetor following the instructions in the manual. Ensure proper fuel shut-off valve operation when storing the generator.
Fuel Stabilizer Usage
Adding fuel stabilizer is vital when storing the Generac RS5500 for extended periods‚ preventing fuel degradation and carburetor issues. Mix the stabilizer with fresh gasoline according to the manufacturer’s instructions – typically‚ one ounce per gallon. Run the generator for a few minutes after adding stabilizer to ensure it circulates.
Stabilized fuel can remain usable for up to a year‚ minimizing starting problems and maintaining optimal performance upon future use. Always refer to the stabilizer’s label for specific guidelines.
Carburetor Cleaning
A clogged carburetor can cause starting difficulties or poor engine performance in the Generac RS5500. If fuel stabilizer hasn’t prevented buildup‚ carefully disassemble the carburetor‚ following the service manual’s instructions. Use carburetor cleaner to dissolve deposits in jets and passages.
Ensure all parts are completely dry before reassembly. Improper cleaning or reassembly can lead to further issues‚ so professional service is recommended if you’re uncomfortable with this process.
Exhaust System Safety
The Generac RS5500 produces deadly carbon monoxide (CO)‚ an odorless and colorless gas. Never operate the generator indoors‚ in partially enclosed spaces‚ or near windows‚ doors‚ or vents. Always position the unit outdoors‚ far from occupied buildings.
Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent CO buildup. Inspect the exhaust system regularly for leaks or damage. A faulty exhaust system can release dangerous levels of CO‚ posing a severe health risk.
Carbon Monoxide Dangers
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a silent killer – odorless‚ colorless‚ and deadly. Exposure to CO can cause flu-like symptoms‚ dizziness‚ unconsciousness‚ and even death. The Generac RS5500 exhaust contains high levels of CO. Never operate this generator indoors or in enclosed spaces.
Install CO detectors with battery backup in your home. If you experience CO poisoning symptoms‚ immediately get fresh air and seek medical attention. Prioritize safety and prevent CO-related emergencies.
Proper Exhaust Ventilation
Ensure adequate ventilation when operating the Generac RS5500. Position the generator outdoors‚ far away from windows‚ doors‚ and vents – at least 20 feet is recommended. Direct exhaust fumes away from occupied buildings and people. Never operate in partially enclosed areas like garages‚ even with doors open.
Regularly inspect the exhaust system for leaks or damage. Maintain clear space around the generator to allow for proper airflow. Prioritize safe exhaust dispersal to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage preserves your Generac RS5500’s reliability. For short-term storage (less than a month)‚ ensure the unit is clean and dry. For long-term storage‚ stabilize the fuel with a fuel stabilizer to prevent degradation. Drain the carburetor if storing for extended periods.
Store in a cool‚ dry‚ and well-ventilated area. Cover the generator to protect it from dust and debris. Disconnect the spark plug wire for added safety during storage.
Short-Term Storage
When storing your Generac RS5500 for a brief period—less than one month—preparation is key. Ensure the generator is completely cool after operation. Clean the exterior surfaces to remove any dirt or debris. Verify the unit is placed on a dry‚ stable surface‚ protected from the elements.
Leave the fuel tank adequately filled with stabilized gasoline. Disconnect any connected appliances. Consider covering the generator with a breathable cloth to prevent dust accumulation.
Long-Term Storage
For storage exceeding one month‚ thorough preparation is crucial. Drain the fuel tank completely to prevent fuel degradation and carburetor issues. Run the engine until it stalls to empty the carburetor. Add fuel stabilizer to a partially filled tank if complete draining isn’t possible.
Remove the spark plug and pour a tablespoon of oil into the cylinder‚ then pull the starter cord several times. Store in a clean‚ dry‚ and well-ventilated area‚ covered to protect from dust.
Electrical Considerations
Proper grounding is essential for safety‚ connecting the generator to a grounded metal pipe or grounding rod. Use heavy-duty‚ outdoor-rated extension cords with the correct gauge for the connected appliances’ amperage. Avoid overloading circuits; calculate the total wattage before connecting devices.
Inspect cords for damage before each use‚ and never use damaged cords. Ensure all connections are secure and dry to prevent electrical shock. Follow all local electrical codes and regulations.
Grounding the Generator
Grounding the generator is crucial for electrical safety‚ protecting against shock hazards. Connect an appropriately sized copper wire from the generator’s grounding terminal to a grounded metal pipe or a grounding rod driven into the earth.
Ensure the grounding connection is secure and free of corrosion. Never attempt to ground the generator to a water pipe or gas line. Consult a qualified electrician if you are unsure about proper grounding procedures.
Extension Cord Usage
Utilize heavy-duty‚ outdoor-rated extension cords when connecting appliances to the Generac RS5500. Ensure the cord’s wire gauge is sufficient for the connected load to prevent overheating and voltage drop. Keep extension cords as short as possible to minimize power loss.
Inspect cords for damage before each use‚ and avoid using damaged cords. Do not overload extension cords or daisy-chain multiple cords together. Always plug the cord into the generator first‚ then the appliance.
Specifications of the RS5500
The Generac RS5500 boasts a running wattage of 5500 watts and a peak wattage of 8000 watts‚ providing ample power for various applications. Its engine is a 4-stroke‚ OHV‚ air-cooled‚ single-cylinder‚ featuring a displacement of 305cc.
The fuel tank capacity is 3.8 gallons‚ offering extended runtimes. It operates on unleaded gasoline. The unit weighs approximately 150 pounds and includes a low-oil shutdown for engine protection.
Wattage (Running/Peak)
The Generac RS5500 delivers 5500 watts of running power‚ suitable for consistent operation of essential appliances and tools. Its peak wattage reaches 8000 watts‚ providing the necessary surge for starting motor-driven equipment.
Understanding these wattage ratings is crucial for preventing overload. Always calculate the total wattage requirements of connected devices before operation‚ ensuring they remain within the generator’s capacity for safe and reliable performance.
Engine Type and Displacement
The Generac RS5500 is powered by a robust 224cc OHV four-stroke engine‚ known for its reliability and fuel efficiency. This engine type delivers consistent power output for various applications.
The displacement of 224cc indicates the total volume swept by the pistons during one complete engine cycle‚ influencing its power and torque capabilities. Regular maintenance‚ as outlined in this manual‚ ensures optimal engine performance and longevity;
Warranty Information
Generac stands behind the quality of the RS5500 with a comprehensive warranty; Typically‚ this includes a limited warranty covering defects in materials and workmanship for a specified period. Please consult the separate warranty document included with your generator for precise terms and conditions.
Warranty coverage may vary based on usage (residential vs. commercial). Proper maintenance‚ as detailed in this manual‚ is crucial for maintaining warranty validity. Register your product online to activate your warranty promptly.
Finding Additional Resources
For further assistance and information regarding your Generac RS5500‚ several resources are readily available. Visit the official Generac website at www.generac.com for FAQs‚ support documentation‚ and contact information. You can also reach Generac support directly at 1-888-436-3722.
Additionally‚ downloadable versions of the RS5500 manual‚ spec sheets‚ and troubleshooting guides can be found on their website. Utilize the product look-up tool using your model or serial number for tailored resources.
Generac Website & Support
Generac’s official website‚ www.generac.com‚ serves as a central hub for RS5500 owners. Explore comprehensive FAQs‚ detailed product documentation‚ and helpful troubleshooting guides. Direct customer support is available via phone at 1-888-436-3722‚ offering expert assistance with any questions or concerns.
The website also features a product look-up tool; simply enter your model or serial number to access specific resources tailored to your RS5500 generator‚ ensuring accurate and relevant information.
RS5500 Manual Download Locations
Access the Generac RS5500 owner’s manual directly from Generac’s website‚ www.generac.com‚ utilizing the product documentation search feature. Alternatively‚ numerous third-party websites archive PDF versions of the manual for convenient offline access. Ensure the downloaded file originates from a reputable source to guarantee accuracy.
Navigating to the product look-up page and entering your generator’s serial number will pinpoint the correct manual version‚ offering the most up-to-date information for your specific unit.
Serial Number Location
Locating the serial number is crucial for accessing specific documentation and warranty information for your Generac RS5500. Typically‚ the serial number is affixed to a label on the generator’s frame. Carefully inspect the unit‚ focusing on the engine compartment and near the model information plate.
Refer to Generac’s online resources‚ specifically the “How Do I Find the Serial Number on My Portable Generator?” article‚ for visual guidance and precise location details.
Understanding the PowerDial Feature
The PowerDial is a central control for starting and operating your Generac RS5500. It allows for selecting between ‘Off’‚ ‘On’‚ and ‘Run’ positions‚ simplifying operation. Ensure the PowerDial is in the ‘Off’ position before performing any maintenance or refueling. Proper use prevents accidental starts and ensures safe operation.
This feature streamlines power management‚ offering a user-friendly interface for controlling the generator’s output. Always consult the full manual for detailed instructions.